Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- English
- 中文
A. Poultry Meat (Chicken and Duck)
It is NOT true at all. Injecting hormones was practised back in the 1970’s and by the 1980’s the use of growth hormones are not permitted any more in livestock. If you happen to see a farmer injecting ‘milky coloured oil’ at the neck, it is not a hormone but a vaccine is being inoculated. Broiler chickens grow faster now mainly due to genetic improvement and the use of well formulated feed.
The use of antibiotics is strictly regulated by the Poison’s Act 1952. They are only used therapeutically on chickens affected by specific diseases and must undergo a withdrawal period before being sold. The claim of being antibiotic free is only a form of quality assurance the producer wants to associate with its brand. It does not say other chickens contain antibiotics.
Generally speaking poultry meats sold in the markets are free from antibiotics. There are government authorities that monitor the situation regularly. The poultry industry as a whole is striving to move away from antibiotics use as growth promoters. They are only used therapeutically under veterinary supervision.
It is not possible to tell from sight alone. The best safeguard is to purchase branded chickens from reputable retail outlets.
It is generally not advisable to repeatedly thaw and freeze chicken meat as it affects quality very significantly. It is much better to divide chicken pieces in cooking portions before the initial freezing and thawed only once before cooking.
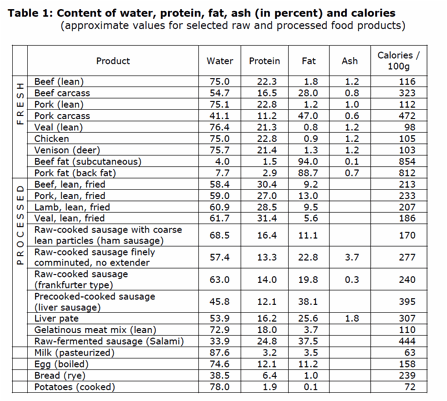
The color of poultry meat is determined by the oxygen transport mechanism to the muscle cells.
Muscles used more frequently, must use myoglobin proteins which can transfer oxygen more efficiently to the muscle cells and get to be dark. This is why non-flying poultry drumsticks have dark meat, while breast meat is white as the medium which transfers oxygen in white meat is glycogen
When dark meat is cooked it turns the myoglobins to metmyoglobins, which is brown/gray.
Dark meats tend to contain more zinc, riboflavin, niacin, thiamin, vitamins B6 and B12, amino acids, iron than white meat. Dark beef contains about 11 times more zinc than tuna, and about 3 times as much iron than raw spinach. Chicken dark meat contain vitamins A, K, B6, B12, niacin, folate, pantothenic acid, minerals as selenium, phosphorus and zinc.
There is not significant difference in the nutritional value of chicken and duck meats. Consumption is largely determined by taste and price affordability.
Chicken liver and intestine are part of the internal organs of the chicken. While some consumers regard them as delicacies, their high minerals, vitamins and fat content in the liver should be taken into account and taken moderately only.
It is a historical fact that Bukit Mertajam was among the first location where broiler chickens were produced in this country. The yellowish color in chickens results from being fed with extra amounts of carotenoids, the precursor for Vitamin A and thus appear to be different from normal chickens. Such chickens can be produced anywhere and is not exclusive to Bukit Mertajam.
A product is only certified halal if it bears the JAKIM logo or the halal mark of the religious authority of the respective state the chicken is sold.
B. Poultry Egg (Chicken and Duck)
A1. Egg is rich in nutrients and a very affordable component of a healthy diet, containing varying amounts of essential vitamins and minerals needed by consumers as well asother beneficial food components.
A3. Different breeds of chickens can lay eggs with shell colour varying from white through brown and to rarer colours such as speckled green. There is absolutely no nutritional differences although there is a preference for one colour over another by different societies and countries.
A9. The level of cholesterol in a person is determined by the sum of cholesterol intake and the amount manufactured by the body. It is safe to take eggs on a daily basis as long as there is a reduction in the intake of other foods containing cholesterol and lipids.
A12. There is no way of knowing the eggs are free from antibiotics. The only way is to test them in the laboratory.
A15. Table 2:
Nutrition Statement | ||
Nutrient or Other Component | Quantity in One Large Egg* | Percent of Daily Value** |
| Calories | 75 | 4 |
| Total Fat | 5 g | 8 |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5 g | 8 |
| Cholesterol | 211.5 mg | 70 |
| Protein | 6.3 g | 13 |
| Vitamin A | 243 IU | 5 |
| Vitamin D | 17 IU | 4 |
| Vitamin E | 0.75 mg | 3 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.6 mcg | 10 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.07 mg | 4 |
| Folate | 24 mcg | 6 |
| Thiamin | 0.031 mg | 2 |
| Riboflavin | 0.24 mg | 14 |
| Phosphorus | 95 mg | 10 |
| Zinc | 0.55 mg | 3 |
| Iron | 0.91 mg | 5 |
| Choline | 125 mg | 22 |
| Lutein & Zeaxanthin | 165 mcg | n/a |
| * Large eggs are the size most commonly sold in the U.S. Eggs of larger or smaller sizes contain proportionally greater or lesser amounts of nutrients. | ||
** Based on 2,000 calorie intake; for adults and children greater than or equal to 4 years of age. Source: www.aeb.org | ||
C. Pork
A1. Prudent use of antibiotic to treat only sick animals is the key principle. Safe pork comes from healthy animal. With proper antibiotic withdrawal period, the antibiotic residue is minimal, and it won’t create human health problems. The government is currently implementing product registration for drugs used in animals, eventually only registered antibiotics will be allowed to be used.
A2. The internal organs of pigs are rich in minerals, vitamins and fat. They are safe to be eaten in moderation and balanced with the intake of other foods.
A3. Eating liver when there is no other protein source available is relatively safe. Since liver has a higher content of minerals and vitamins as well as fat its intake should be reduced proportionately with the intake of other protein foods.
A8. According to the Pig Farmers Association self surveillance program which is done twice a year, and recognized by the Department of Veterinary Services (DVS), the incidence of using illegal beta agonist is now minimal, with only few cases detected out of 565 farms inspected. We still continue to educate our members not to use illegal compound and aims to reach zero misuse eventually.
If in doubt, call DVS hotline at 03-88702000
D. General Questions
A. 家禽肉类(鸡肉与鸭肉)
A1. 这是完全不正确的。肉鸡注射荷尔蒙发生在1970年代,但自1980年代起,成长荷尔蒙便不被准许用在任何禽畜身上。倘若您发现一名农民正在注射一种”牛奶色的油”在鸡颈,那不是荷尔蒙而是在接种疫苗。肉鸡现在成长较快,主要是因为遗传改良以及更好的饲料配方。
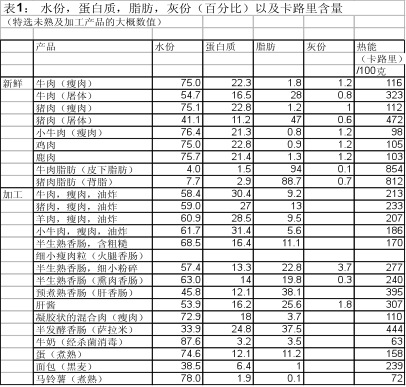
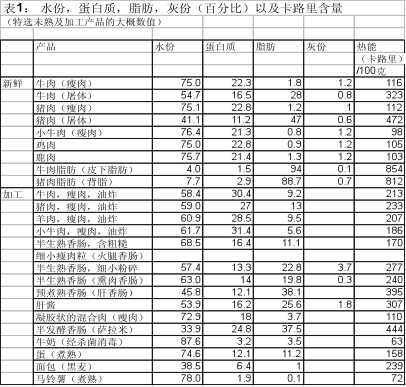
A9. 禽肉的颜色是由肌肉细胞的氧气输送系统来决定的。肌肉通常必须通过肌红蛋白更有效地输送氧气至肌肉细胞,并使到鸡肉较深色。这是为何不会飞的家禽腿肉颜色较深,而胸肉颜色较白,因为白肉输送氧气的媒介是肝醣。
当深色肉在烹煮时,它将肌红蛋白转为变性肌红蛋白,其色为褐色/灰色。
深色肉比白肉倾向于含有较多的锌,核黄素,烟酸,维生素B1, B6 及B12,氨基酸,铁质。深色牛肉比金枪鱼含有多11倍的锌,以及比生菠菜多3倍的铁。鸡肉的深色肉含维生素A, K, B6, B12, 烟酸,叶酸,泛酸,矿物质如硒,磷和锌。
A10. 鸡肉和鸭肉的营养价值并无很大的差异。人们是根据其味道和价格来决定消费。
资料来源:兽医局[/caption]
B. 家禽蛋类(鸡蛋与鸭蛋)
A1. 蛋的营养丰富,并且是一个负担得起的健康饮食,富含各种人体所需的必须维生素和矿物质以及其他有益的成份。
A4. 后院式农场和封闭式农场(battery caged) 生产的蛋味道稍有不同。这主要是因为饲料来源有异;后院饲养的土鸡吃的是从四周环境取得的食物而养在笼里的鸡则食用商业性饲料配方。一般农场都有兽医局的卫生鉴定计划,督查农场正确使用任何药品,而且此鉴定计划亦减少沙门氏杆菌污染鸡蛋的机率;反而后院饲养的土鸡蛋沙门氏杆菌污染的机率更高。
A6. 欧美加3是在蛋黄内。像其他食物一样,应适量以及和个人的生活方式相称的食用蛋类。体力活跃者可以多吃因为他们燃烧较多的卡路里。
A9. 一个人的胆固醇水平是由胆固醇摄入量以及人体所生产的胆固醇数量所决定。只要减少其他含胆固醇和油脂食物的摄入量,每天吃蛋是安全的。
| 营养列表 | ||
| 营养或其他成份 | 在一粒大蛋中的数量* | 每日数值 百分比** |
|---|---|---|
| Calories 卡路里 | 75 | 4 |
| Total Fat 总脂肪 | 5 g | 8 |
| Saturated Fat 饱和脂肪 | 1.5 g | 8 |
| Cholesterol 胆固醇 | 211.5 mg | 70 |
| Protein 蛋白质 | 6.3 g | 13 |
| Vitamin A 维生素 A | 243 IU | 5 |
| Vitamin D 维生素 D | 17 IU | 4 |
| Vitamin E 维生素 E | 0.75 mg | 3 |
| Vitamin B12 维生素 B12 | 0.6 mcg | 10 |
| Vitamin B6 维生素 B6 | 0.07 mg | 4 |
| Folate 叶酸 | 24 mcg | 6 |
| Thiamin维生素 B1 | 0.031 mg | 2 |
| Riboflavin 核黄素 | 0.24 mg | 14 |
| Phosphorus 磷 | 95 mg | 10 |
| Zinc 锌 | 0.55 mg | 3 |
| Iron 铁 | 0.91 mg | 5 |
| Choline 胆碱 | 125 mg | 22 |
| Lutein & Zeaxanthin 叶黄素与玉米黄质 | 165 mcg | 不详 |
| * 大蛋是在美国最普遍售卖的蛋。较大或小粒的蛋营养照比例。 | ||
| ** 根据 2,000 卡路里的摄入量;成人及4岁或以上的儿童。 | ||
C. 猪肉
A8. 根据养猪公会受兽医局承认并一年进行两次的养猪农场自我监察计划,使用非法乙型受体素的发生率很小,在565家受检农场中仅有数宗而已。我们仍然持续的教育会员切勿使用非法药物并且在最终达到零乙型受体素的目标。
若有任何疑问,请联络兽医局热线号码:03-88702000。